December solstice
21 December will be the shortest day of 2020 in the northern hemisphere, midwinter day.
This is the day when the Sun’s annual journey through the constellations of the zodiac reaches its most southerly point in the sky, in the constellation of Capricornus at a declination of 23.5°S. This day is counted by astronomers to be the first day of winter in the northern hemisphere.
In the southern hemisphere, the Sun is above the horizon for longer than on any other day of the year, and astronomers define this to be the first day of summer.
At the solstice, the Sun appears overhead at noon when observed from locations on the tropic of Capricorn, at a latitude 23.5°S.
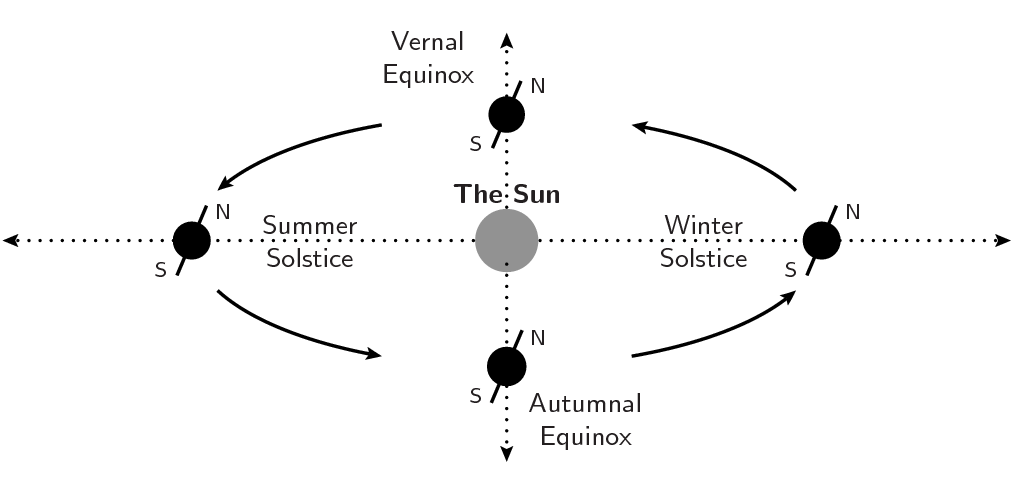
Solstices occur because the axis of the Earth’s spin – its polar axis – is tilted at an angle of 23.5° to the plane of its orbit around the Sun.
The direction of the Earth’s spin axis remains fixed in space as it circles around the Sun, while the Earth’s sight line to the Sun moves through the constellations of the zodiac. As a result, sometimes the Earth’s north pole is tilted towards the Sun (in June), and at other times it is tilted away from it (in December). This gives rise to the Earth’s seasons: